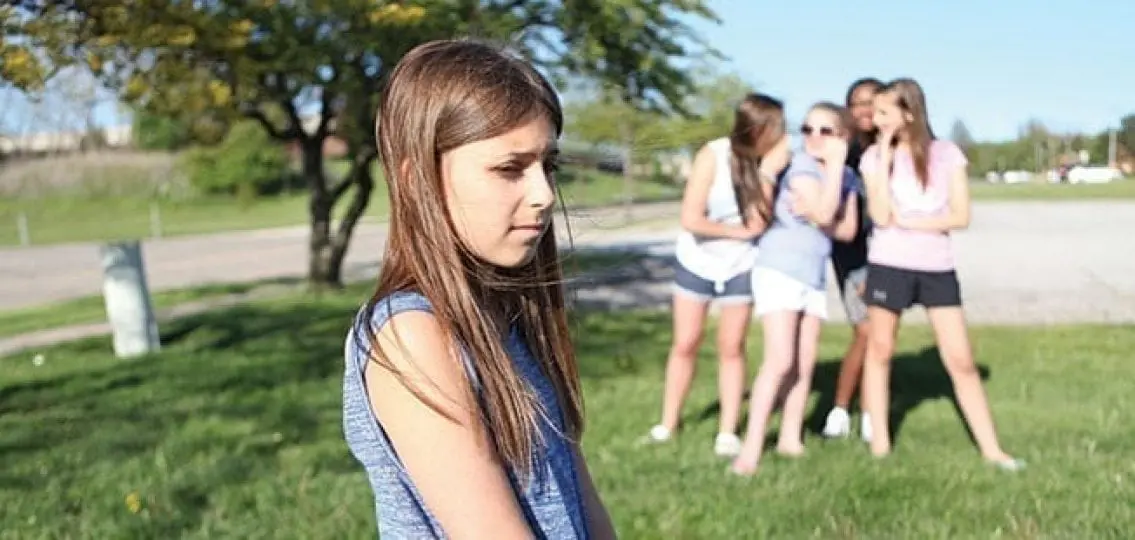Your son or daughter is being tormented by students at school. Snide comments, nasty rumors, and eye-rolling have all become part of your child’s life. Your child has become increasingly depressed and often does not want to go to school.

When you discussed these concerns with the principal, he or she may have indicated an intent to help make things better, but your child continues to get bullied at school. Alternatively, you may have heard such comments as: “This isn’t bullying.” “They were just joking.” “Your child is overreacting.” “Your child needs to learn to deal with it.” “If your child would stop (describe behavior), this wouldn’t happen.”
But anytime any concerns around bullying in school become public, an administrator will issue a statement. “Our district has zero tolerance to bullying.” The approach schools have been directed to use to reduce bullying in school is not working.
State statutes make bullying a violation of the disciplinary code. For necessary protection of students accused of bullying, strict definitions have been incorporated. Further, principals are unlikely to impose discipline based solely on the complaints of another student. Schools are also under great pressure to reduce suspensions. In some states, schools are required to make annual reports of bullying incidents—which are considered black marks.
As a result, we see a very absurd, negative impact. In 2016, 71 percent of New York City schools reported zero bullying incidents. However, in a state survey, the percentage of students reporting they had been bullied rose from 11.7 percent in 2011, when the NY bullying statute was enacted, to 20.6 percent in 2015.
Helping a Bullied Child: 8 Steps for Parents
To more effectively support and empower your child who is getting bullied , and to ensure an effective response by the school, you are advised to:
1. Document hurtful behavior.
Document that hurtful behavior directed at your child is happening in an intentional and repeated manner. This may include repeated aggression from one or a small group of students or may be more wide-spread. This could also include denigration by a school staff member.
2. Document Civil Rights violations.
If your child is a member of a protected class under civil rights laws, which includes race, religion, or national origin; disabilities; or sexual harassment (including gender orientation or identity), document how the harassment appears to be grounded in your child’s status.
3. Identify those nearby.
Identify people who were nearby and describe how they responded. Include staff members and students who may have witnessed the hurtful incidents.
4. Outline the impact.
Outline how this is negatively impacting your child, including your child’s emotional distress and school avoidance. Obtain a letter from your pediatrician describing the harmful impact.
5. Present documentation.
Present this documentation to the principal. Alternatively, if the principal has a history of not responding effectively, contact the district office and ask to meet with a district level staff person who addresses issues of bullying. If this is unsuccessful, reach out to the state department of education. If your child is a member of a protected class, also ask for the civil rights coordinator.
6. Ask for a response.
Make it clear you are not asking for the aggressors to be suspended. Insist they be held accountable, accept personal responsibility, and take steps to remedy the harm. This is called “restorative practice.” Also insist that your school take comprehensive action to assess and address the hostile environment.
7. Empower your child.
Empower your child to remain calm and respond with strength, but not aggression, if someone is hurtful. Remind your child that it is not always possible to control what happens, but they do have the power to control how they feel about themselves and respond. Focus on mindfulness and relationship problem-solving skills. Encourage your child to reach out to be kind to other students at least 5 times a day.
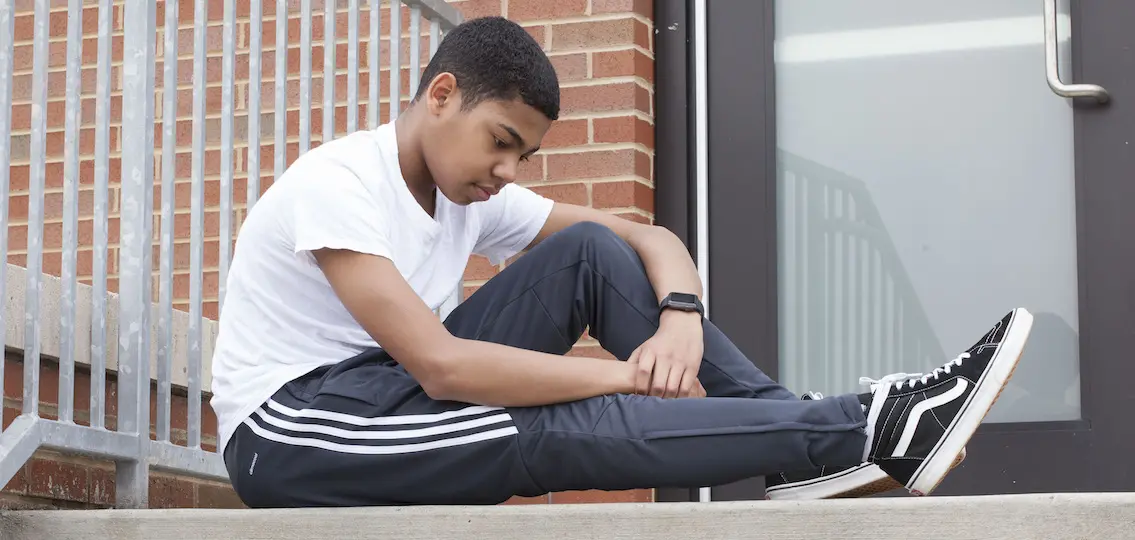

8. Involve yourself with school organizations.
Become involved with your school’s parent organization, to encourage your school to focus on positive school climate, student leadership, social emotional learning, cultural competence, and embracing a culture of kindness and civility. Promote the importance of conducting regular surveys to assess school climate and bullying.