I remember counting down the days until summer break started. In my daily planning calendar for school I had a countdown with the days remaining in the school year. Now, decades later, it is very interesting to experience the anticipation leading to summer break as a parent. In some ways, you look forward to having the kids at home for the summer. However, as parent, the idea of being responsible for keeping your kids occupied during the summer can be daunting.
My kid’s excitement for summer break is no surprise at all. After months of hard work, they finally get a chance to relax, hang out with friends, travel, and pull out their summer outfits. But just how long is summer break, really? In this article, we’ll answer that question and show you a table with the average summer break length for each U.S. state. While the exact dates can change a little, you’ll see that summer break usually lasts about the same amount of time no matter where you live.
How Long is Summer Break in the United States?
In the United States, the average summer break is about 10 to 11 weeks long, which is around 2.5 months. Most schools finish up in late May or early June and start back in early to mid-August. Although the exact dates can be a little different depending on where you live, the overall length is pretty much the same in every state.
How Long is Summer Break in Each State?
In most states, the average summer break is between 10 and 11 weeks. However, there are some states where the average is 9 weeks and others where the average is 12 weeks. Look at the state by state breakdown in the table below.
| State | Average Summer Break (Weeks) |
| Alabama | 10 weeks |
| Alaska | 11 weeks |
| Arizona | 10 weeks |
| Arkansas | 11 weeks |
| California | 10 weeks |
| Colorado | 11 weeks |
| Connecticut | 9 weeks |
| Delaware | 9 weeks |
| Florida | 10 weeks |
| Georgia | 10 weeks |
| Hawaii | 9 weeks |
| Idaho | 11 weeks |
| Illinois | 11 weeks |
| Indiana | 10 weeks |
| Iowa | 11 weeks |
| Kansas | 10 weeks |
| Kentucky | 11 weeks |
| Louisiana | 11 weeks |
| Maine | 9 weeks |
| Maryland | 10 weeks |
| Massachusetts | 9 weeks |
| Michigan | 10 weeks |
| Minnesota | 12 weeks |
| Mississippi | 10 weeks |
| Missouri | 11 weeks |
| Montana | 11 weeks |
| Nebraska | 11 weeks |
| Nevada | 10 weeks |
| New Hampshire | 9 weeks |
| New Jersey | 9 weeks |
| New Mexico | 11 weeks |
| New York | 10 weeks |
| North Carolina | 11 weeks |
| North Dakota | 11 weeks |
| Ohio | 11 weeks |
| Oklahoma | 10 weeks |
| Oregon | 10 weeks |
| Pennsylvania | 10 weeks |
| Rhode Island | 9 weeks |
| South Carolina | 10 weeks |
| South Dakota | 11 weeks |
| Tennessee | 10 weeks |
| Texas | 12 weeks |
| Utah | 11 weeks |
| Vermont | 9 weeks |
| Virginia | 10 weeks |
| Washington | 10 weeks |
| West Virginia | 11 weeks |
| Wisconsin | 12 weeks |
| Wyoming | 11 weeks |
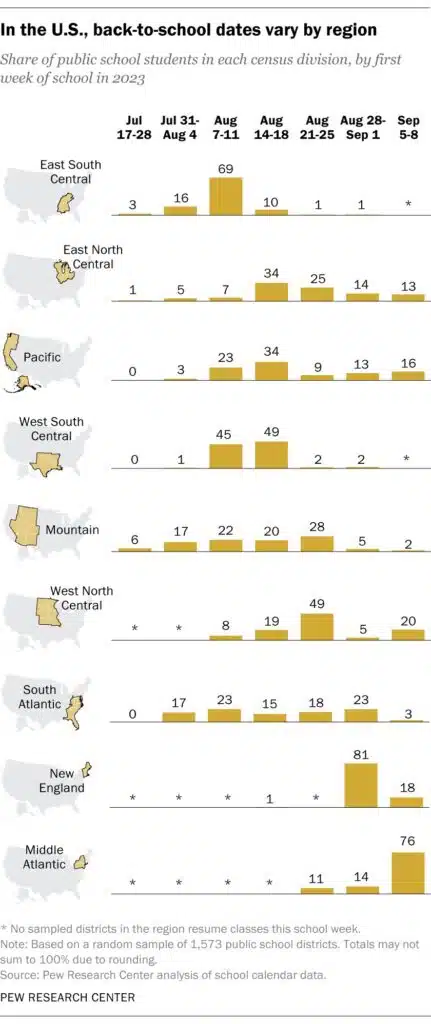
Pew Research did an analysis of school calendar data and has a great graphic about the varying start dates between regions in the United States. Check it out below, and read the full summer break story on pew research for more information.
Why do different schools and school districts have different summer breaks?
Different schools and school districts have different summer breaks because each one sets its own calendar based on what works best for their community. Things like state rules, local weather, and even how many snow days they usually get can all play a part in deciding when school starts and ends. Some areas prefer to start school earlier in August, while others wait until after Labor Day.
Some schools even follow a year-round schedule with shorter breaks throughout the year instead of one long summer break. One of the biggest factors impacting summer break is weather and the school’s facilities. If the school is in a state or city that experiences particularly hot summers and they don’t have strong enough air conditioning, they might choose to have summer break to cover the hottest months. That way, students won’t be exposed to an environment that is too hot.
How do I figure out how long summer break is at my school?
To find out how long summer break is at your school, you can start by counting the number of days between the last day of the current school year and the first day of the next one. For example, if your last day of school is May 27 and your first day back is August 12, your summer break would be 77 days long which is 11 weeks.
If you’re not sure exactly when school ends or starts again, it’s a good idea to ask your school or your school district. They usually post the official school calendar online, so there’s a good chance you can find that information on your school’s website. Knowing the length of your summer break is crucial for planning vacations and making the most out of your summer.
Should Summer Break be Longer or Shorter?
Benefits of having a longer summer break
Almost every student would like a longer summer break. It gives families more time to travel, visit loved ones, and cross items off of their summer bucket list. It also gives students a real chance to rest and recharge after a long year of studying, homework, and activities. Plus, having extra time away from school pressures can be great for mental health. For academically advanced students, summer break can be an opportunity to take summer classes and get ahead in their studies.
Downsides of having a long summer break
While a longer summer break might sound exciting, it can come with some real challenges for students and families. One major issue is learning loss. When kids are out of school for too long, they can forget what they learned in subjects like math and reading. This means teachers often have to spend the first few weeks of the new school year going over information from the previous school year. Another problem is childcare. Many parents work year-round, and a longer break can make it harder to find affordable care or activities for their kids during those extra weeks. For some students, school is where they get regular, healthy meals. Without access to school breakfast and lunch programs, a longer summer can make it even tougher for families who already struggle with food insecurity.